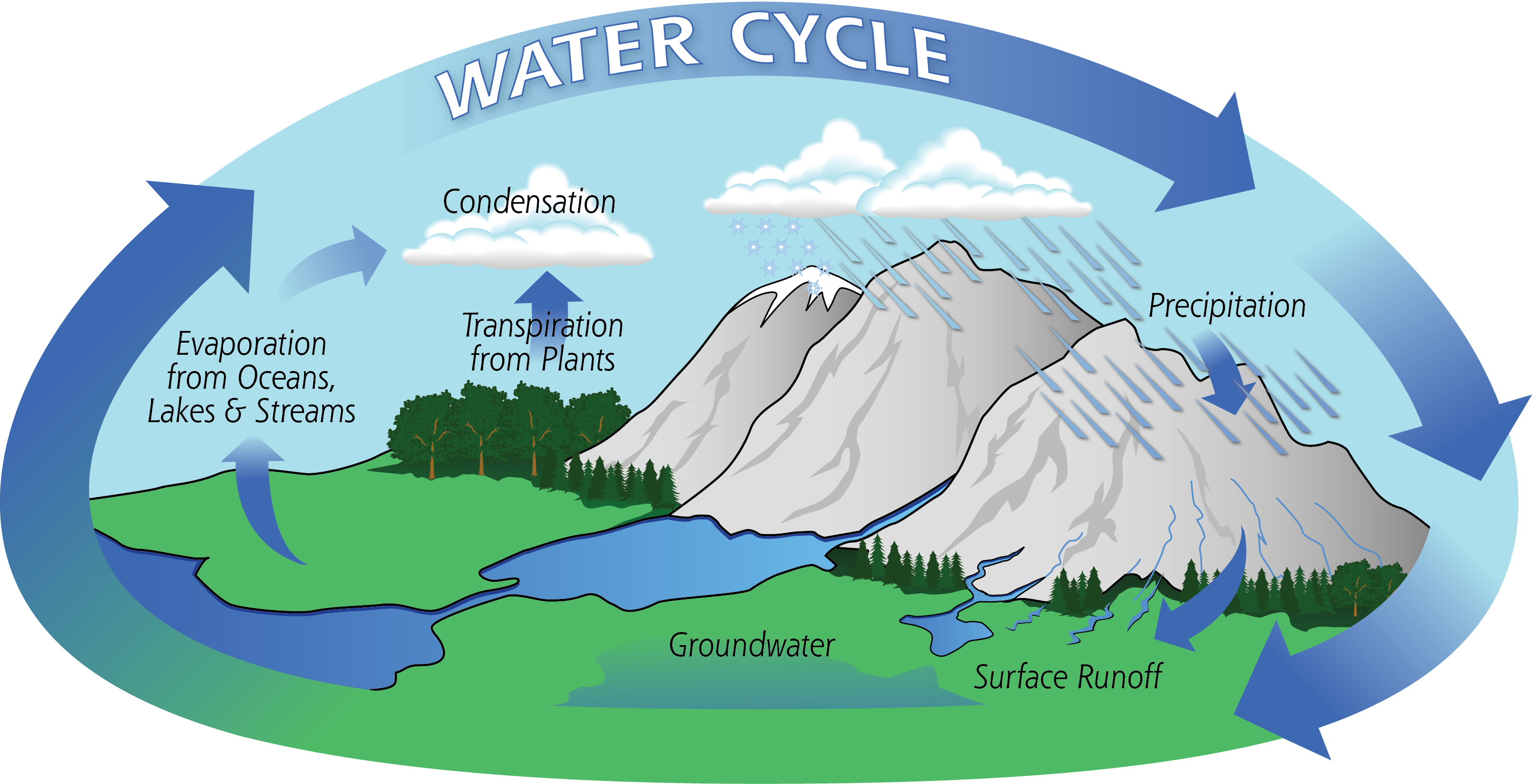
Solar Energy
Aim: To learn about how solar energy is used.
Hypothesis: I think that silver will attract the most heat because, when the light shines on silver it will reflect on it.
Materials:
- White Paper
- Styrofoam Cup (X2)
- Clear Cup
- Roll of Tinfoil
- Black plastic
- Lamp
- Thermometer
Steps
- Gather all materials.
- Put down some paper, tin foil and a piece of black plastic on the table.
- Wrap some tin foil on one styrofoam cup.
- Cut a circle piece of black plastic and wrap around a clear cup.
- Put each cup on eat coloured material. etc. Black, white and silver.
- Set down lamp and face towards cups. Make sure lamp is on.
- Wait every 15 minutes and use thermometers to record the temperature.
Findings:
Conclusion:
- solar is a renewable item because this helps us to make electricity by not killing the coal and you can reuse the solar because the son will keep going for a billion of years and we can still save the earth.
- The sun, water, and wind can help us to make energy because here in New Zealand we use water so we have energy and wind can help us make the windmill spins and the solar energy can get energy from the sun
- in our other experiment the black make heat and this is
- The wind is a renewable energy because it does run out.
- It costs more to my coal rather than solar power.
- Solar is better than coal because solar can live up to billions of years